- Overview
- Creating Report Tables
- Viewing Stored in a Report Table
- Editing Report Tables
- Deleting Report Tables
- Regenerating Data Reports
- Importing Report Tables
- Exporting Report Tables
- Including System Variables in Report Tables
- Querying Report Tables
- Querying Report Tables in Dynaforms
- Querying Report Tables in Triggers
- Querying the Current Case in Dynaforms
- Exporting Checkgroups
- Exporting Data in Report Tables
Overview
The information entered into Dynaform fields and case variables are stored as serialized strings, which are not easy to access with database queries. Report Tables are designed to put case data into a format that can be easily accessed by standard SQL queries or external applications. Report Tables also allow case data to be easily queried in Dynaform fields and shared with external reporting tools, such as Crystal Reports, Jasper Reports and Pentaho Reporting.
Each time a new case is created, a new record will be added to the Report Table. This record will be updated each time a Dynaform is submitted in the case.
Unsupported Fields
The following controls cannot be used in report tables because they can contain multiple values and are stored differently:
- Checkgroup. See Exporting Checkgroups.
- File fields in grids. File type fields cannot to be selected if the report table type is "Grid".
Creating Report Tables
| Warning: Before creating a report table, remember that the variables included in your process must follow the rules in the Naming Variables section to avoid conflicts. |
To create a new Report Table, open the process where it will be used, then go to the Process Objects toolbox at the right-hand side of the process map. Hover the pointer of the mouse over the ![]() icon of the Report Tables option and click on the Create button that is displayed to the left:
icon of the Report Tables option and click on the Create button that is displayed to the left:
A window will be displayed where the properties of the new report table can be defined.
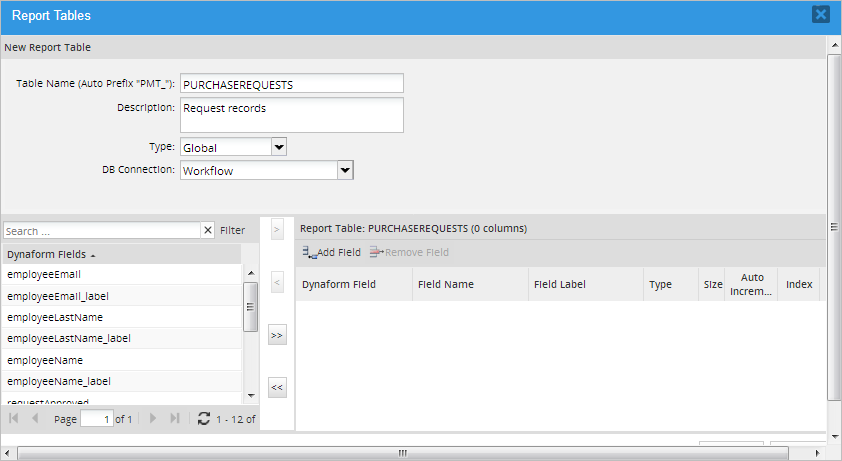
-
Table Name: Enter the name of the Report Table.
Note: To avoid issues when entering a name of a Report Table, follow the best practices as in naming variables.
- Description: Enter a brief description of the report table's content.
- Type: Select the type of data that will be exported to the report table.
-
Global: Export data stored in variables used by Dynaform fields and/or any case variables defined in triggers. This option allows individual variables to be selected for export.
After selecting this option, select which case variables will be exported by clicking the field name and clicking the
 button. To select multiple fields, hold down the CONTROL or SHIFT keys while clicking on the field names and click on
button. To select multiple fields, hold down the CONTROL or SHIFT keys while clicking on the field names and click on  to add the selected fields to the report table. Click on
to add the selected fields to the report table. Click on  to add all the fields to the report table. To remove a field from the report table, select the field name in the right-hand table and click on
to add all the fields to the report table. To remove a field from the report table, select the field name in the right-hand table and click on  , or click on
, or click on  to remove all the variables from the report table.
to remove all the variables from the report table.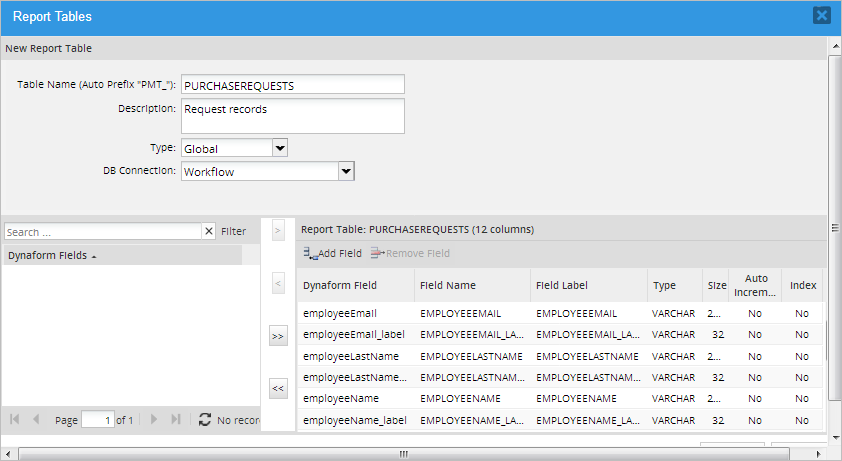
In addition to the fields selected by the user, three system variables fields are included by default to indicate which case is related to which field values in the wf_<workspace>.APPLICATION table.
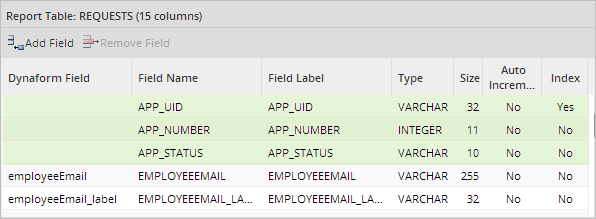
- APP_UID: The case's unique ID. This value is used to obtained the case information. This field can NOT be removed from the report table.
- APP_NUMBER: The case number. Report tables use this value to relate the case information with an individual case. This field can NOT be removed from the report table.
- APP_STATUS: The case status. This field can be removed from the report table if desired.
-
Grid: Export data from a grid. This option lets the user select individual fields from the grid. After selecting "Grid" in the Type field, a new dropdown will be displayed where the grid can be selected. Note that a grid is only listed if a variable is assigned to it.
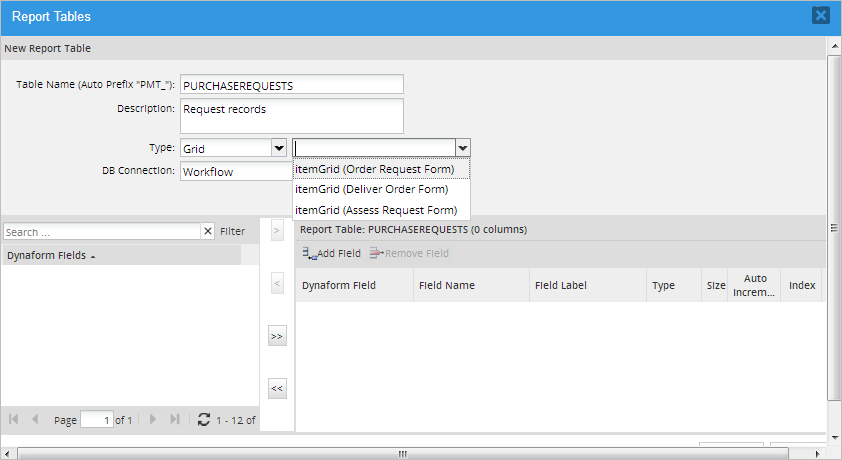
After selecting a grid, all its fields will be listed in the Dynaform Fields column at the left.
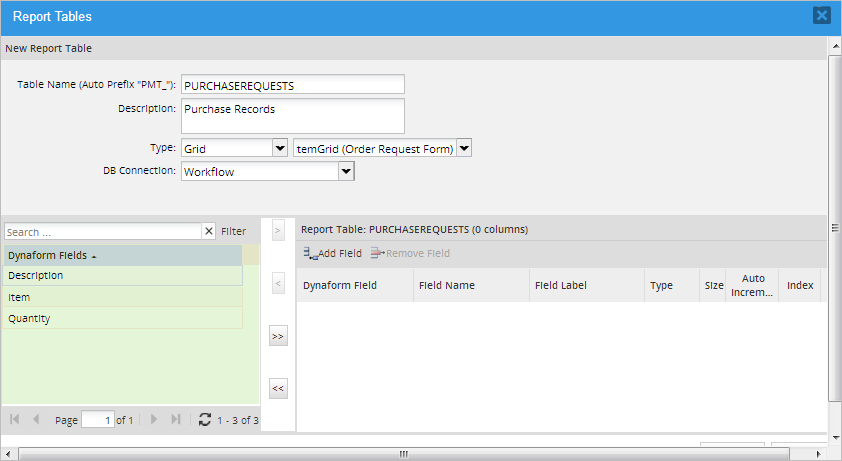
Select the grid fields to be included in the report table by clicking on the field name and clicking the
 button. To select multiple fields, hold down the CONTROL or SHIFT keys while clicking the field names and click on
button. To select multiple fields, hold down the CONTROL or SHIFT keys while clicking the field names and click on  . Click the
. Click the  button to add all the fields to the report table. To remove a field from the report table, select its name from the list at the right of the window and click on
button to add all the fields to the report table. To remove a field from the report table, select its name from the list at the right of the window and click on  , or click on
, or click on  to remove all the variables from the report table.
to remove all the variables from the report table.In addition to the fields selected by the user, four system variables fields are included by default to indicate which case is related to which field values in the wf_<workspace>.APPLICATION table.
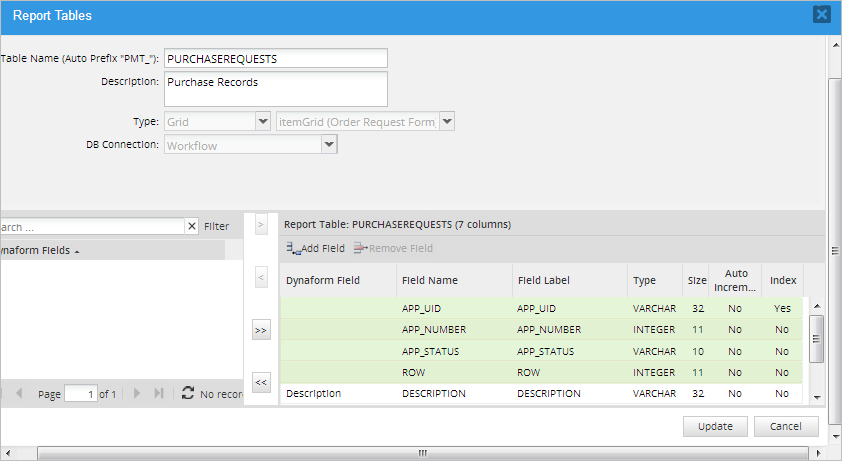
- APP_UID: The case's unique ID. This value is used to obtained the case information. This field can NOT be removed from the report table.
- APP_NUMBER: The case number. Report tables use this value to relate the case information with an individual case. This field can NOT be removed from the report table.
- APP_STATUS: The case status. This field can be removed from the report table if desired.
- ROW: Row number of the grid.
These four fields are added by default and can NOT be removed from the report table.
-
DB Connection: Select the database connection used to store the new report table.
- Workflow: The report table will be stored in the wf_<WORKSPACE> database of the current workspace.
- Report: This option will only appear if the workspace was imported from ProcessMaker version 2, which used 3 databases per workspace. The report table will be stored in the rp_<WORKSPACE> database of the current workspace.
- Another database: The report table can be stored in any database that has a Database Connection.
Note: It is only possible to create Report Tables in MySQL databases. The list will only show connections to those databases even if the project has connections to other DBMS.
The order of the fields can be changed by dragging and dropping a field from one position to another in the list. It is possible to change the Field Name, Field Label, Type, Size and Index properties of a field by double clicking on the row to edit it.
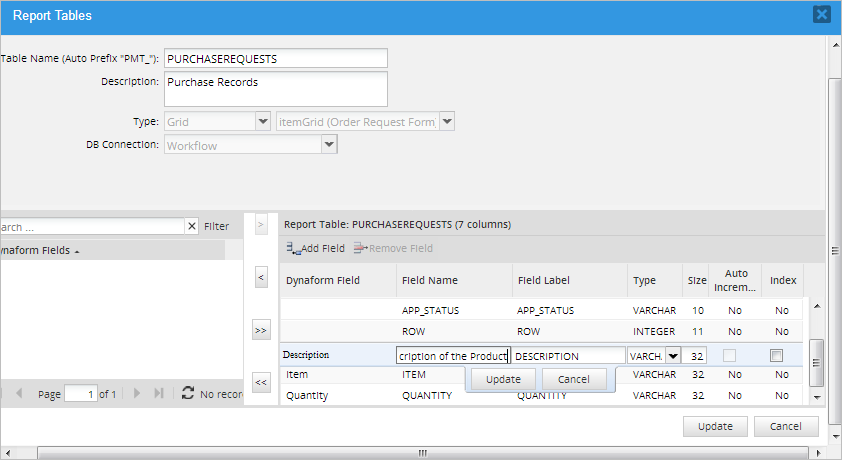
Marking the Index option will index the field so its data can be searched faster. It is NOT recommended to reduce the size of VARCHAR fields, because they only use as much space as needed to hold their data, so there is no benefit to reducing the size of the field (VARCHAR fields hold up to 255 characters).
By default, the field names are in upper case and cannot be changed to lower case. Remember that MySQL databases are case-sensitive by default in Linux/UNIX. It is generally recommended to leave the field names as they are.
Note: Take into account the following recommendations about the field name:
ALTER, CLOSE, COMMIT, CREATE, DECLARE, DELETE, DROP, FETCH, FUNCTION, GRANT, INDEX, INSERT,
OPEN, REVOKE, ROLLBACK, SELECT, SYNONYM, TABLE, UPDATE, VIEW, APP_UID, ROW, PMTABLE, TIME
Or one of these reserved words in PHP:
case, catch, cfunction, class, clone, const, continue, declare, default, do, else, elseif, enddeclare, endfor, endforeach,
endif, endswitch, endwhile, extends, final, for, foreach, function, global, goto, if, implements, interface, instanceof, private,
namespace, new, old_function, or, throw, protected, public, static, switch, xor, try, use, var, while
When done defining the new report table, click on the Create button at the bottom of the panel. The new table will be created and populated with data from all the existing cases of the current process. The new table will be added to the list of available Report Tables (not only inside the project but also in Admin > Settings > PM Tables).
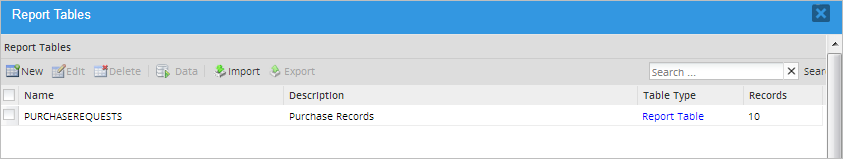
The new report table will be stored in the database with a PMT_. prefix (e.g. PMT_CONTACT_INFO). Remember to include PMT_ in the table name when using the table in SQL queries and external report applications.
Note: If an error occurs when populating a report table, the error is registered in the error log. All records populate the report table except those that presented issues. Therefore, the report table might not match with the number of cases created in the process.
Viewing Stored in a Report Table
To view the data stored in a Report Table, click on the Report Tables option in the Process Objects toolbar on the process map to see a list of the available Report Tables.
A window will open with a list of the existing report tables.
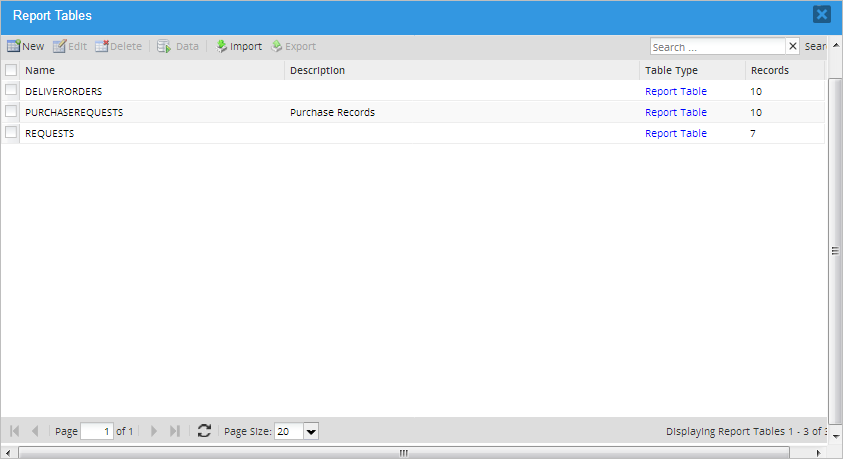
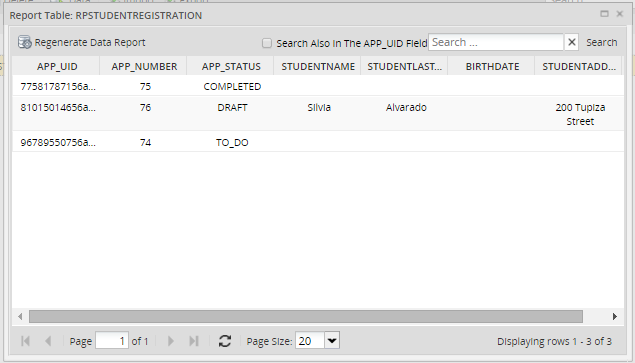
Select a report table from the list and click on the Data button in the top menu. A window will open displaying the contents of the report table, which is the information filled in by the end users while running cases.
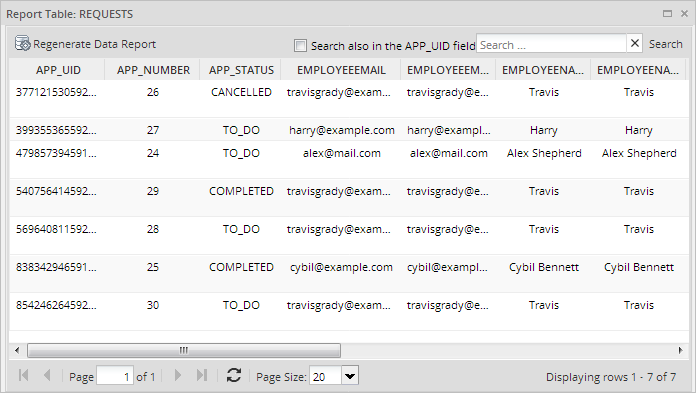
Searching Data Inside a Report Table
To find specific values inside a report table, enter the text to be searched in the Search box, which is located in the upper right-hand corner of the Data window. The search criteria can contain either text or numbers, but it is not possible to include special characters, such as < (less than), > (greater than), % (percentage), etc.
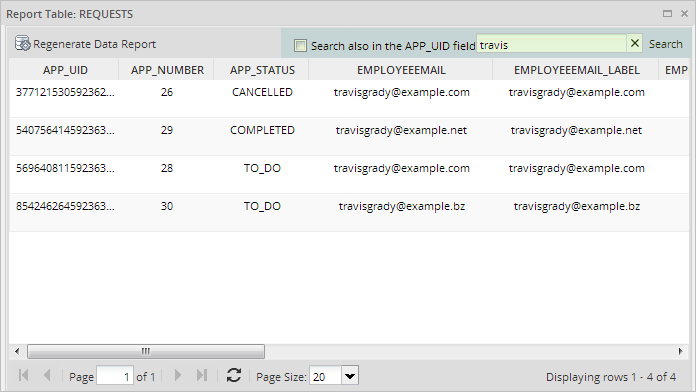
The search criteria inserted can be searched in the following columns:
- APP_UID: Check Search also in the APP_UID field to include this column in the search. Search for the case's unique ID number, which is 32 hexadecimal characters long. It is possible
to search for only part of the number. For instance, the first 5 numbers in a UID:
55101. - APP_NUMBER: Search for a case number.
- APP_STATUS: Search using the case status, which can be
TO_DO,DRAFT,PAUSED,CANCELLED,COMPLETEDorDELETED. - Dynaform fields: Searches can be conducted in any of the other fields in the report table, except for datetime fields, which are not supported as search criteria.
Editing Report Tables
Choose one table and click on Edit to alter its field structure, or change the table's name or description. All properties can be edited, but take into consideration that edits can cause data loss. In the same way, altering the data structure can cause data incompatibility, lock tables or external events. It is recommended to proceed carefully, taking reasonable steps such as backing up, stopping data traffic, and other measures.
Note: For Stacks that uses Job Schedulings. If updating the Report Table, first stop the jobs, after updating the Report Tables start the jobs again.
Note: In ProcessMaker 3.4.X with Stack 240, after editing and adding new Dynaform fields to a Report table, the record data lose. In ProcessMaker 3.5.X with Stack 270, the previous behavior has been fixed.
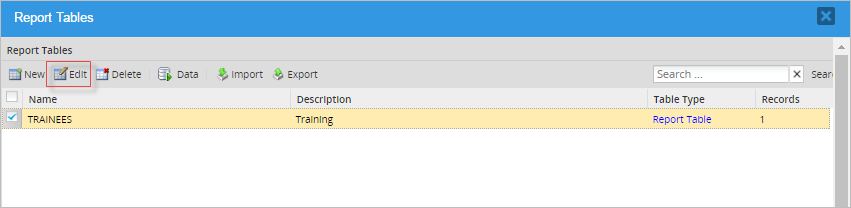
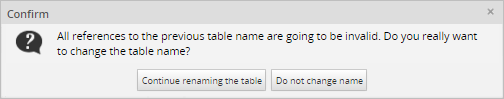
When editing a Report Table's name:
A message will ask for confirmation.
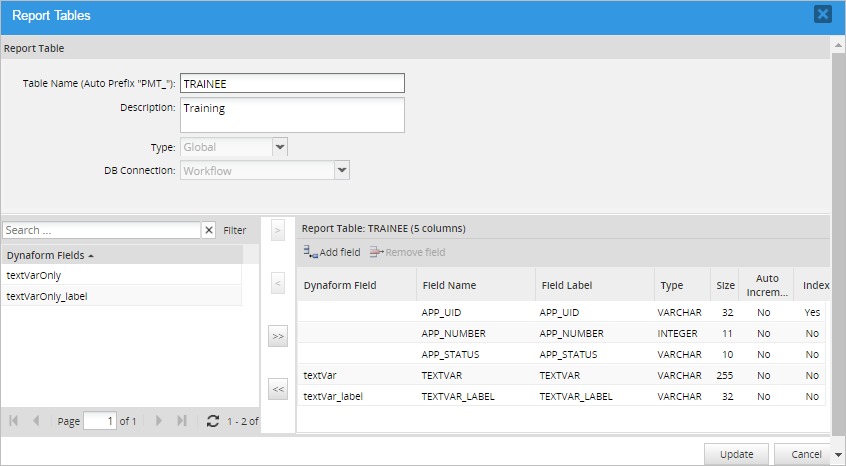
If a new field is added to a master Dynaform, or its field name is changed, the definition of the Report Table will NOT automatically update to include the new/changed field. The definition of the Report Table will have to be manually updated to include the new/changed field.
For example, using the trigger above, change the caseTask name to caseTaskID and also change its name in the trigger to @@caseTaskID. Then, go to Report Tables and select the name of the Report Table. Click Edit and the modified field will be displayed in the list of Dynaform fields as a new field.
If a field is added or changed in a grid form, then the existing Report Table will have to be deleted and then recreated to include the new/changed fields. The new field or information will be updated automatically in the database.
Deleting Report Tables
To delete a Report Table, open the process and click on the Report Tables option in the Process Objects toolbox. Select a Report Table in the list and click on the Delete button in the top menu to remove it it from the list and delete its table in the database.
Regenerating Data Reports
Use this option to manually update any data modified while running cases. Go to the list of Report Tables and choose the one to regenerate by clicking on Data. After the data from the specific Report Table is displayed, click on the Regenerate Data Report option at the top of the window.
Consider that while cases are being created and routed, data is created and updated in the Report Tables; therefore, it is not necessary to use the Regenerate Data Report option each time.
Asynchronous Regeneration
Available Version: As of ProcessMaker 3.5.0.
In the PM Tables interface, the Report Tables regenerate data asynchronously. All changes made during the data regeneration are batched using a customized value in the Task Manager. Therefore, the user can make any other actions in ProcessMaker while this task runs in the background.
Configure in the env.ini file the number of rows by that Report Tables batches by adding the following line:
- Where
#numberis the number of rows. It must be an integer value no lower than1.1000value is the default value when thereport_table_batch_regenerationparameter is not used in theenv.inifile.
Note: If problems occur when populating the information of the Report Tables in either operating system you are working: CentOS or Windows, stop and start the supervisor according the explanation of the Upgrade Standard Procedure to ProcessMaker 3.6.x. Then, the regeneration of the table will have the correct information.
Importing Report Tables
To import a Report Table, click on the Report Tables option in the Process Objects toolbox and the list of Report Tables available will be displayed. Select a Report and click on the Import option. In the window that opens, click on the file button to select a Report Table from the computer. Remember that like PM tables, Report Tables have the .pmt extension.
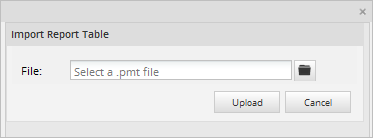
Once the Report Table has been imported, the corresponding table will be created in the wf_<WORKSPACE> database, depending on the DB connection previously chosen.
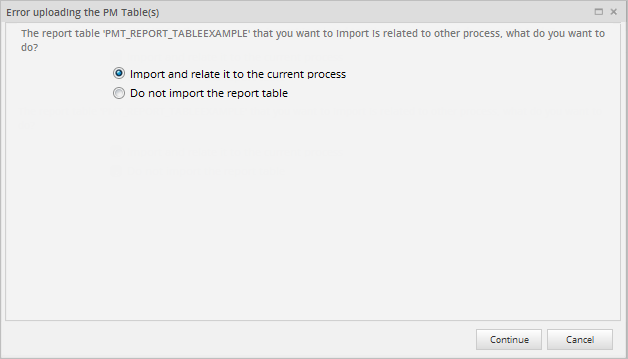
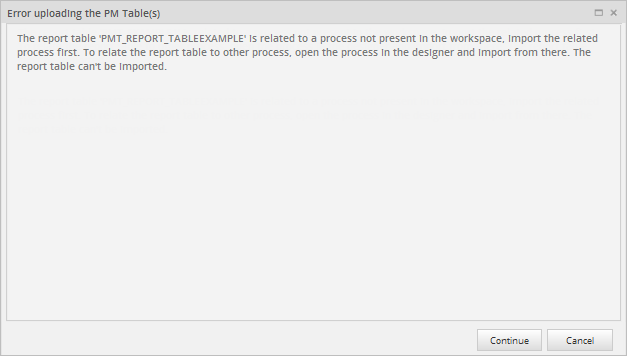
When importing a Report Table that is related to a different process, a warning message appears with the following options:
- Import and relate it to the current process: The Report Table will be imported and related to the current process.
- Do not import the Report Table: To stop importing the Report Table.
If a Report Table already exists, a window will show the following options for each conflicting Report Table:
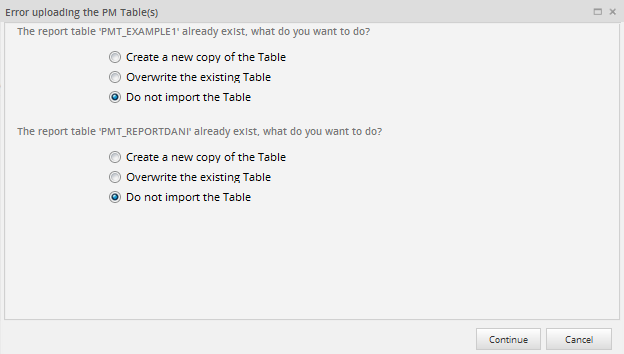
- Create a new copy of the Table: The Report Table will be imported with a name composed of the original name
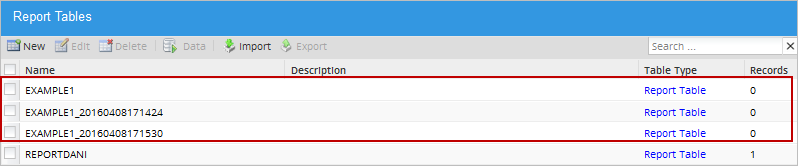
plus the current datetime. For example: if the Report table EXAMPLE1 is being imported, but the same table already exists in the workspace, the Report Table will be imported as EXAMPLE1_20160408171424 where the name includes the:
- Date: 20160408: Year-Month-Day
- Time: 171424: Hour-Minute-Seconds
- Overwrite the existing Table: The existing PM Table will be overwritten by the imported one.
Note: Before overwriting a Report table with the same table structure, ensure to generate and save data that could be lost in the importing process.
- Do not import the Report Table
It is also possible to import a Report Table by going to Admin > Settings > PM Tables and selecting the Import option in the toolbar.
However, this option is only available for Report Tables related to processes in the current workspace. Otherwise, the following error message will be displayed:
Exporting Report Tables
Note: It is recommended to export PM Tables and Report Tables separately.
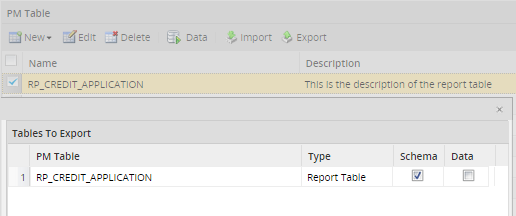
To export a Report Table, click on the Report Tables option in the Process Objects toolbar and the list of Report Tables available will be displayed. Select the report table to export and click on Export. A window with two options will be displayed:
- Schema: After checking this option, the Report Table will be exported with the field structure but no data.
- Data: Data export for Report Tables is not allowed because the data comes from cases, and information stored in cases can't be exported.
Like PM tables, the export files of Report Tables have the .pmt extension.
Including System Variables in Report Tables
System variables, such as @@TASK or @@USER_LOGGED, are not available in the list of variables that can be included in Report Tables. These values may be useful for queries based upon a particular user, task, process, etc.
To export a system variable, create a trigger that will assign the value of a system variable to a case variable. For example:
@@caseUserName = @@USR_USERNAME;
@%caseIndex = @%INDEX;
@@caseTask = @@TASK;
@@caseProcess = @@PROCESS;
Then, set the trigger to fire at various points in the process where the exported table should be updated with new values for the system variables. Remember that the values of system variables change over the course of a case, so the trigger should be fired whenever the new values need to be exported to the Report Table. After defining the trigger, change the definition of the Report Table to include the new case variables that were defined in the trigger.
Querying Report Tables
Report Tables can be queried with the Sql property in Dynaform fields or by calling the executeQuery() function in triggers.
To query a Report Table in a Dynaform field, first set the SQL Connection property for the field to the database where the Report Table is stored. If it is in the wf_<WORKSPACE> database of the current workspace, then either set it to workflow or leave it blank. If it is in the rp_<WORKSPACE> database of the current workspace, then select report (for workspaces migrated from version 2 to version 2.8). For any other database (including databases in other workspaces), first create a database connection to that database, and then select it in the Sql Connection property.
Querying Report Tables in Dynaforms
In the field's Sql property, enter a SELECT statement to query the Report Table. Remember that the Report Table has the prefix PMT_ in its table name. If populating a dropdown, listbox, suggest box, checkgroup or radiogroup, remember that the SQL query needs to return two fields, where the first field is the value and the second field is the label for each option.
Example:
Get a list of all the clients used in previous cases for a suggest box, so that users do not have to remember the full name of clients when filling in a form. If the Report Table is named CLIENTS and has the fields CLT_ID, CLT_FIRSTNAME and CLT_LASTNAME, then the following query can be used to populate the suggest box:
DISTINCT is used to eliminate duplicates and the second field is a concatenation of the client's first and last names, so both can be displayed in the suggest box.
Querying Report Tables in Triggers
The executeQuery() function can be used to query Report Tables in Triggers. In the Report Table, each case is stored as a separate record in the APP_UID, APP_NUMBER and APP_STATUS fields, so that it is possible to search for data from specific cases.
Example:
In this example, a grid is populated with data from the current case and all cases that currently have TO_DO status. The trigger queries a Report Table named PRODUCTS, which has the fields PRO_NAME, PRO_TYPE and PRO_DESC. The Report Table is stored in a remote database that has a database connection with the UID of "17848610856943f64e405e8058194105".
First, create a grid named "products", which contains the textbox fields "productName", "productType" and "productDescription". Then, create a trigger with the following code to populate the @=products variable, which is used by this grid:
$currentCase = @@APPLICATION;
$query = "SELECT PRO_NAME AS productName, PRO_TYPE AS productType, PRO_DESC AS productDescription
FROM PMT_PRODUCTS WHERE APP_UID = '$currentCase' OR APP_STATUS = 'TO_DO' ";
@=products = executeQuery($query, $db);
Note that it is not possible to insert case variables in the middle of strings like normal PHP variables, so first assign the case ID in @@APPLICATION to the $currentCase variable so it can be inserted into the SQL query. Since the fields in the Report Table have names different from the fields in the grid, they have to be renamed using AS. Remember that field names in grids are case sensitive, so "productType" is different than "ProductType" and "PRODUCTTYPE".
The database query returns an associative array of associative arrays, which is also how grids are stored in ProcessMaker. For example, this database query might return the following data, which is placed in the grid:
'1' => array("productName" => "E-Z PencilMate", "productType" => "Office supplies", "productDescription" => "Holds multiple pencils"),
'2' => array("productName" => "Brite 30W Lamp", "productType" => "Office furniture", "productDescription" => "Upright lamp with shade"),
'3' => array("productName" => "Sleeptite pillow", "productType" => "Bed assessory", "productDescription" => "Goose feather pillow")
)
Set the above trigger to fire BEFORE the Dynaform that contains the "products" grid. When the Dynaform is displayed while running a case, the grid should be populated with data from the current case and from previous cases with "TO_DO" status.
Querying the Current Case in Dynaforms
To use the unique ID of the current case in an SQL query of a Report Table, create a hidden field in the Dynaform named "APPLICATION". When the Dynaform is rendered while running a case, the unique ID of the current case stored in the @@APPLICATION system variable will automatically be placed in the "APPLICATION" field where it can be used in SQL queries.
Example:
A textarea field needs to display all the users who have worked on the current case in a dropdown box, so that the current user can select the user who will be assigned to the next task in the process. The following SQL query looks up all the users who have worked on the current case by using the current case's UID stored in the "APPLICATION" hidden field.
FROM USERS U, APP_DELEGATION AD WHERE AD.APP_UID = @@APPLICATION AND AD.USR_UID = U.USR_UID
Exporting Checkgroups
Checkgroups are designed to hold multiple values, so they can't be stored very easily in Report Tables. It is possible to create a trigger that converts the values stored in these fields to JSON strings and stores them in string variables. These string variables can be included in the Report Table, like other variables. The difficulty of storing them as JSON strings is that they have be converted from JSON to an object to read them. This means that the values can't be viewed easily using just the database software. Almost all programming languages have a JSON decode function, such as JSON.parse() in JavaScript, json_decode() in PHP and json.loads() in Python, but this means that code will have to be executed before viewing the values.
The other option is to manually create another table in the database to hold the values stored in these fields. A trigger can be used to export the variables used by checkgroups to this table. Using a separate table allows the values to be viewed with ordinary database software and accessed with normal SQL queries. See the following instructions to implement either of these solutions.
Storing as JSON Strings
To store the values of checkgroups as JSON strings, first add an additional string variable for each checkgroup or grid. Then, add a trigger that is set to fire after the Dynaform that contains the checkgroups. Convert the values of the checkgroups into JSON strings and save them in the string variables. Then, add those string variables to the Report Table.
A process has the "selectCountry" checkgroup and the "clientsList" grid:
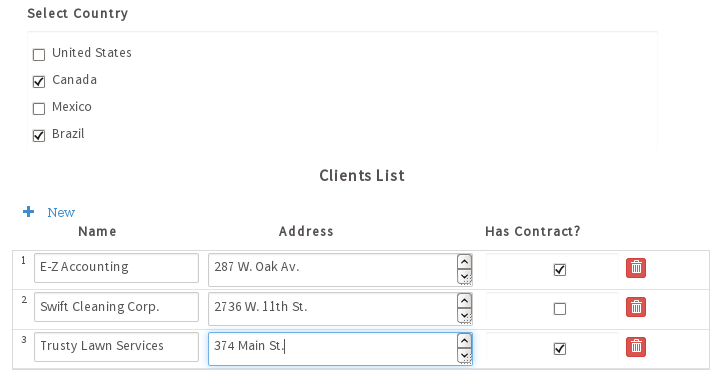
Add two string variables named "selectCountryValuesJson" and "selectCountryLabelsJson" to hold the values and labels of the selected options in the "selectCountry" checkgroup. Also add a string variable named "clientsListJson" to hold the grid converted to a JSON string.
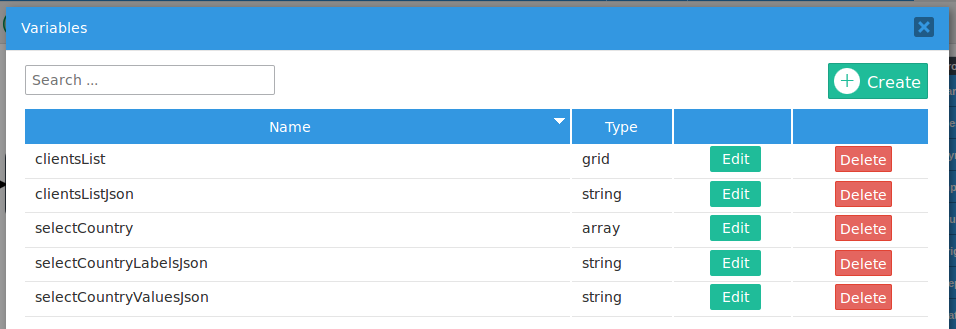
Then, create the following trigger to store the values of these grids as JSON strings in the string variables:
@@selectCountryValuesJson = json_encode(@=selectCountry);
@@selectCountryLabelsJson = @@selectCountry_label; //already a JSON string
//export a grid as a JSON string:
@@clientsListJson = json_encode(@=clientsList);
Set this trigger to execute after the Dynaform that contains the checkgroup and grid. Then add the selectCountryValuesJson, selectCountryLabelsJson and clientsListJson variables to the Report Table so they will automatically be exported by ProcessMaker when cases are run.
The values and labels selected in a checkbox are generally not difficult to read with the human eye. For example, the "selectCountryJson" and "selectCountryJsonLabels" variables might contain:
It is easier to read when spacing is added:
"1": {
"name": "E-Z Accounting",
"name_label": "E-Z Accounting",
"address": "287 W. Oak Av.\r\nLong Branch NJ 87364",
"address_label": "287 W. Oak Av.\r\nLong Branch NJ 87364",
"hasContract": "1",
"hasContract_label": "true"
},
"2": {
"name": "Swift Cleaning Corp",
"name_label": "Swift Cleaning Corp",
"address" : "2736 W. 11th\r\nWest Palm Beach FL 38725",
"address_label": "2736 W. 11th\r\nWest Palm Beach FL 38725",
"hasContract" : "0",
"hasContract_label": "false"
},
"3" : {
"name": "Trusty Lawn Services",
"name_label": "Trusty Lawn Services",
"address": "371 Main St.\r\nCloverdale IN 46135",
"address_label": "371 Main St.\r\nCloverdale IN 46135",
"hasContract": "1",
"hasContract_label": "true"
}
}
When these variables are automatically exported to the Report Table as JSON strings, they will probably need to be decoded. For example, the following trigger code pulls these values from the Report Table named "PMT_CLIENT_INFO" with a database query using executeQuery(). In a previous Dynaform, the user enters the number of the case whose values should be copied into the "selectCountry" and "clientsList" variables of the current case. The json_decode() function is used to decode the JSON strings. When decoding the grid, the second parameter of json_decode() is set to true to convert an object to an associative array.
$query = "SELECT SELECTCOUNTRYVALUESJSON, SELECTCOUNTRYLABELSJSON, CLIENTSLISTJSON
FROM PMT_CLIENTS_INFO where APP_NUMBER = '$caseNo' ";
$result = executeQuery($query);
if (is_array($result) and count($result) > 0) {
@=selectCountry = json_decode($result[1]['SELECTCOUNTRYVALUESJSON']);
@@selectCountry_label = $result[1]['SELECTCOUNTRYLABELSJSON'];
@=clientsList = json_decode($result[1]['CLIENTSLISTJSON'], true);
}
Storing Grids in a Separate Table
Another way to export a grid is to create a separate table to hold the values entered into the grid's fields. To store the values in ProcessMaker, a PM Table can be created to hold these values, or a table can be created in an external database.
For example, if using the "clientsList" grid from the previous example, then create a PM Table named CLIENTS_LIST with the following fields: APP_UID, APP_NUMBER, ROW_NO, NAME, ADDRESS, HAS_CONTRACT.
Then, create the following trigger to write the values in the grid to the PM Table:
//look up the case number (and case status if needed):
$result = executeQuery("SELECT APP_NUMBER, APP_STATUS FROM APPLICATION WHERE APP_UID='$caseId'");
$caseNo = $result[1]['APP_NUMBER'];
//first delete all existing records from this case, if updating:
executeQuery("DELETE FROM PMT_CLIENTS_LIST WHERE APP_UID='$caseId' ");
//then insert a new record for each row in the "clientsList" grid
for ($rowNo = 1; $rowNo <= count(@=clientsList); $rowNo++) {
$name = @=clientsList[$rowNo]['name'];
$address = @=clientsList[$rowNo]['address'];
$hasContract = @=clientsList[$rowNo]['hasContract'];
$query = "INSERT INTO PMT_CLIENTS_LIST (APP_UID, APP_NUMBER, ROW_NO, NAME, ADDRESS, HAS_CONTRACT)
VALUES ('$caseId', '$caseNo', $rowNo, '$name', '$address', '$hasContract')";
executeQuery($query);
}
Set the above trigger to execute after every Dynaform that contains the "clientsList" grid.
Exporting Data in Report Tables
ProcessMaker currently doesn't support the export of the data in Report Tables. However, it is possible to export the data in a Report Table (or PM Table) using PhpMyAdmin.
Direct the web browser to the installation of PhpMyAdmin on your server, which is generally found at:
http://IP-ADDRESS/phpmyadmin
Enter with the "root" user. Then, go to the wf_WORKSPACE database (which is named wf_workflow by default) in the left sidebar. Then, select the Report Table, which will have the prefix PMT_, to open it.
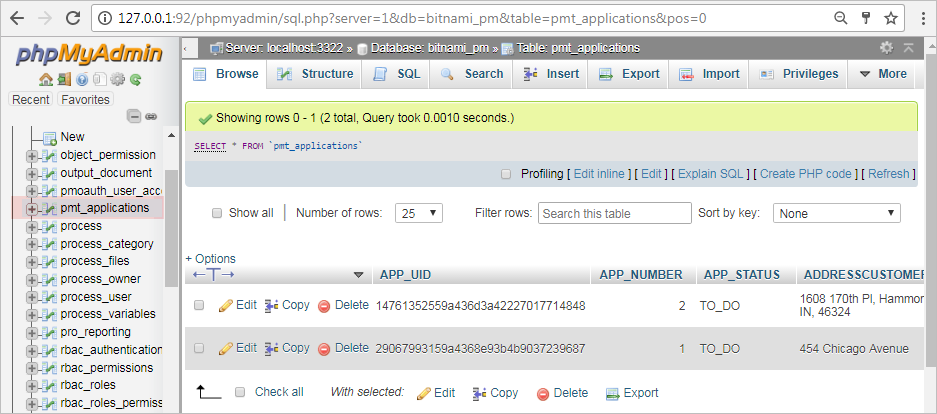
Once the table is open, click on the Export tab in the top menu. Then, select the Format of the data file to export.
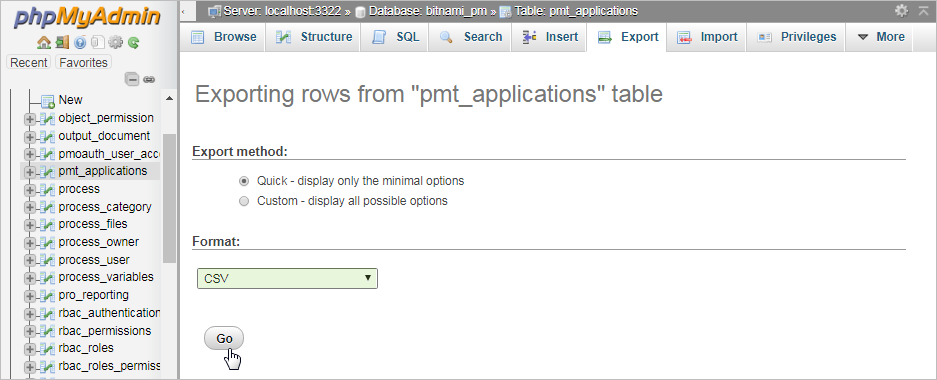
Finally, click on Go at the bottom and it should generate a CSV file that can be imported to any spreadsheet or database.
It is recommended to select CSV for MS Excel if using Microsoft Office and OpenDocument spreadsheet if using OpenOffice or LibreOffice.
Exporting Report Tables with Triggers
It is also possible to export a Report Table (or PM Table) from a process by using trigger code to query the Report Table and construct a CSV (Comma Seperated Values) file, which the user can download. This file can then be opened by any spreadsheet or database program. The advantage of using triggers is that ordinary users can obtain the CSV file without the security risk of giving the user access to PhpMyAdmin.
To see a sample process that uses triggers to export Report Tables, download and import Export_Report_Table_or_PM_Table_as_CSV_File-3.pmx (right click on this link and select "Save as..."). Remember to assign users to the first task of the process to run cases of this process.
To add this functionality to an existing process, first add an Input Document to the process where the CSV file will be uploaded after it is created with a trigger. Then, edit a Dynaform and add a dropdown box whose ID and variable are named "reportTableName".
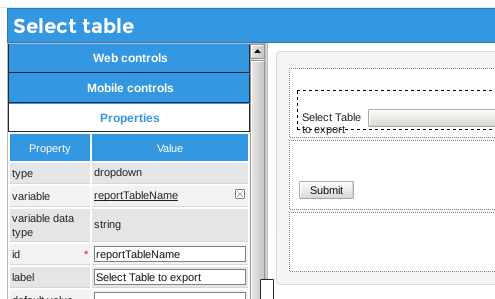
Set its sql property to the query:
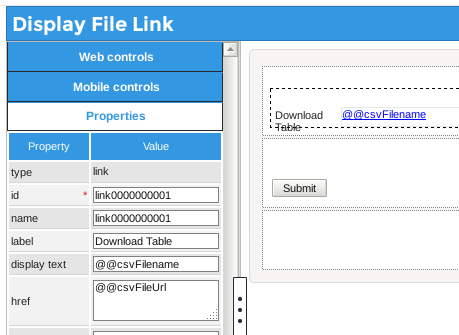
@@csvFilename variable and set its href property to
the @@csvFileUrl variable. These two variables will be set by trigger code and automatically inserted
into the Link field when the Dynaform is generated during a case.
Then, create a trigger that will query the database to get the contents of the Report Table or PM Table selected by the user in the first Dynaform. Add the following code to the trigger:
// Function to prepare the value from char fields for export
// by escapeing " (double quotation marks) by doubling them and
// replacing '\r\n' with a hard return "\n", which occurs in textareas.
// If necessary, the value is enclosed in "..."
function escapeValue($s) {
$s2 = str_replace('"', '""', $s);
$s2 = str_replace('\r\n', "\n", $s2);
if ($s != $s2 or trim($s2) != $s2) {
$s2 = '"'. $s2 .'"';
}
return $s2;
}
if (empty(@@reportTableName)) {
die("Please select table to export.");
}
$reportTbl = @@reportTableName;
$aFields = executeQuery('DESCRIBE ' . $reportTbl) or
die("Error: Unable to find table '$reportTbl'.");
$aFieldNames = array();
foreach ($aFields as $aField) {
$aFieldNames[] = $aField['Field'];
}
$firstLine = implode('; ', $aFieldNames);
$aRows = executeQuery("SELECT * FROM $reportTbl") or
die("Error: Unable to query table '$reportTbl'.");
$aExportRows = array($firstLine);
foreach ($aRows as $aRow) {
$aExportLine = array();
foreach ($aFields as $aField) {
$val = $aRow[ $aField['Field'] ];
if (strpos($aField['Type'], "char") !== false) {
$val = escapeValue($val);
}
$aExportLine[] = $val;
}
$aExportRows[] = implode(';', $aExportLine);
}
@@sContents = implode("\n", $aExportRows);
$csvFilePath = tempnam(sys_get_temp_dir(), $reportTbl . '_') . '.csv';
@@csvFilename = basename($csvFilePath);
file_put_contents($csvFilePath, @@sContents);
//upload CSV file to Input Document:
$params = array (
'APPLICATION' => @@APPLICATION,
'INDEX' => @@INDEX,
'USR_UID' => @@USER_LOGGED,
'DOC_UID' => $InputDocId,
'APP_DOC_TYPE' => 'INPUT',
'TITLE' => 'CSV file',
'COMMENT' => "CSV file for table $reportTbl",
'ATTACH_FILE' => '@' . $csvFilePath
);
//URL to upload files
$baseUrl = (G::is_https() ? "https://" : "http://") . $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'] .
($_SERVER['SERVER_PORT'] == '80' ? '' : ':'.$_SERVER['SERVER_PORT']) . //comment out if no port
'/sys' . @@SYS_SYS;
$url = $baseUrl . '/en/neoclassic/services/upload';
ob_flush();
$ch = curl_init($url);
// curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_VERBOSE, 1); //Uncomment to debug
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, 1);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, 1);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $params);
// curl_setopt ($ch, CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYHOST, 1); //Uncomment for SSL
// curl_setopt ($ch, CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER, 1); //Uncomment for SSL
@@response = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
if (strpos(@@response, "uploaded successfully") !== false) {
$path = explode('*', @@response)[0];
$filename = basename($path, '.csv');
$fileId = explode('_', $filename)[0];
@@csvFileUrl = $baseUrl . '/en/neoclassic/cases/cases_ShowDocument?a=' . $fileId . '&v=1';
unlink($csvFilePath);
}
else {
die("Error uploading file '$csvFilePath' to $url:\n\n" . @@response);
}
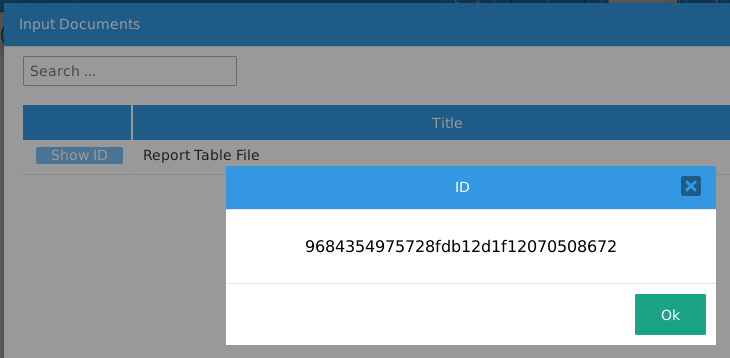
Set this trigger to execute before the second Dynaform that contains the Link field. Make sure to change the $InputDocId variable to the unique ID of the Input Document, which can be found by clicking on its Show ID button when viewing the list of Input Documents.
In this trigger, the first time executeQuery() is called, it looks up the structure of the Report Table or PM Table selected by the user. It uses this information to create the first line of the CSV file that holds the names of the fields in the table.
The second time executeQuery() is called, it obtains the contents of the table to be exported. The code then loops through each row in this table and copies the data to the $aExportRows array. To export this information correctly, data is passed through the escapeValue() function if the field is a char or varchar, so it might need to have its data enclosed in "" (double quotation marks).
Then, the records in the $aExportRows array are converted into a string with the implode() function. This content is written to a temporary file whose filename is the name of the table plus a randomly generated code. Then, the cURL library is used to upload the temporary file to the Input Document. If the file was successfully uploaded, then the response message will be similar to this text:
The trigger uses explode() and basename() to break up this message and obtain the unique ID of the uploaded file, which in this example is "2930668665729a4e185c473029977042". This ID is used to construct the URL to download the file, which will be something like:
http://example.com/sysworkflow/en/neoclassic/cases/cases_ShowDocument?a=2930668665729a4e185c473029977042&v=1
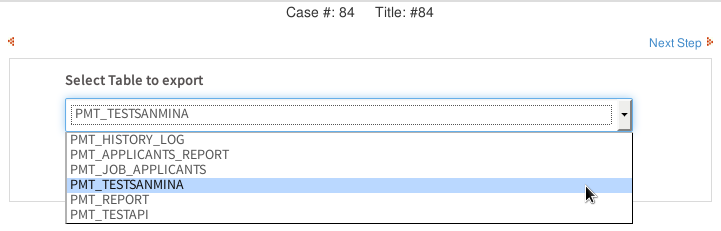
When a case is run, the user will first select the table to export:
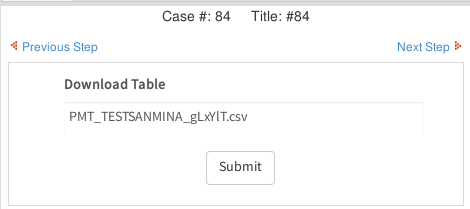
Then, the second Dynaform will contain a link to download the generated CSV file:
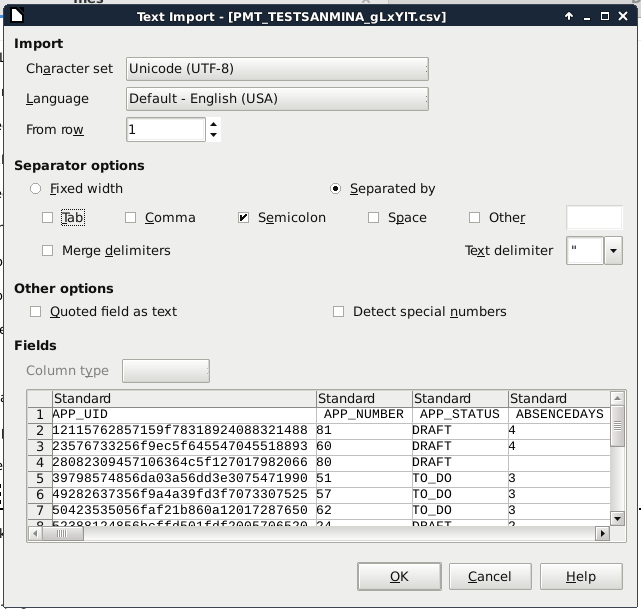
Click on the link to download the CSV file to the local computer. When opening the CSV file in a spreadsheet program, make sure to select the UTF-8 character set and make sure that the values are separated by semicolons. For example, when opening the CSV file in OpenOffice or LibreOffice, the following settings are selected when importing the file: