- Using the
processmakercommand - List of options
- Help for an option
- ProcessMaker Commands
- artisan
- browser-cache-files-upgrade
- build-js
- cacheview-repair
- change-password-hash-method (Enterprise only)
- check-queries-incompatibilities
- check-workspace-disabled-code (Enterprise only)
- clear-dyn-content-history-data
- convert-old-web-entries
- database-upgrade
- database-verify-consistency
- database-verify-migration-consistency
- documents-add-font
- documents-list-registered-fonts
- documents-remove-font
- flush-cache
- hotfix-install
- info
- mafe-translation
- migrate-cases-folders
- migrate-content
- migrate-history-data
- migrate-indexing-acv
- migrate-itee-to-dummytask
- migrate-list-unassigned (Enterprise only)
- migrate-new-cases-lists (Enterprise only)
- migrate-plugins-singleton-information
- plugins-database-upgrade
- plugins-translation-create
- plugins-translation-update
- remove-unused-files
- translation-repair
- unify-database (Enterprise only)
- upgrade
- upgrade-content
- workspace-backup
- workspace-restore
- workspace-upgrade
The processmaker command is used to perform maintenance tasks in ProcessMaker. Because some of these tasks involving altering the file structure, it is required to have root or administrator access in order to run the processmaker command.
Using the processmaker command
In the server where ProcessMaker is installed, login as the root user or administrator. On Windows systems, start the command prompt as the administrator. On Linux/UNIX systems, open a terminal and login as root user or use the sudo command to gain root privileges:
To avoid permission problems when running processmaker command in Linux, run the processmaker command using the Apache/NGINX user permissions. To do so, ownership of the ProcessMaker directory must belong to apache or nginx, so that Apache/NGINX can read and write data. The -R makes the ownership changes recursive (apply to all files and directories within /opt/processmaker).
- Apache:
chown -R apache:apache /opt/processmaker - NGINX:
chown -R nginx:nginx /opt/processmaker
Then, use the cd command to switch the directory where ProcessMaker is installed. The location may vary depending on your system:
Linux/UNIX:
Windows - Bitnami Installer:
Note: Bitnami is no longer used in ProcessMaker as of version 3.4.0. This must be considered when accessing the ProcessMaker directory.
Note: The AppData directory is a hidden directory, but the File Explorer can be configured to show hidden files.
The processmaker command can be issued from the base directory of the processmaker installation:
For Windows system (Bitnami Installer), it may be necessary to specify the path to the php.exe file:
Note: To avoid writing out the path to php.exe, add the PHP directory to the PATH system variable.
List of options
To see the list of options available for the processmaker command, issue the command with the help option.
For example, on a Linux/UNIX system:
Help for an option
To display help for an option of the processmaker command, issue the command in this way:
For example to get help for the database-upgrade option:
ProcessMaker Commands
The following sections describe all ProcessMaker commands.
artisan
Available Version: As of ProcessMaker 3.4.0
This command runs Artisan, which loads the workspace parameters. This command works in the ProcessMaker background using Queue system architecture. In this way, you can work without having delays nor problems with run and reporting errors in:
- Intermediate Email Events
- End Email Events
- ProcessMaker Functions (PMFSendMessage, PMFSendMessageToGroup)
For ProcessMaker functions, take into account:
- All Parameters send through the trigger function normally. However, the behavior changes when the function returns an integer number for confirmation: instead of confirming an email has been sent through the email server, the
artisan queue:workcommand adds the ProcessMaker function in the queue with a0or1to confirm for the job was created. - The
artisan queue:workcommand queues the ProcessMaker Function but not the trigger itself. - The
artisan queue:workcommand queues ProcessMaker functions asynchronously without an option to set functions to not work without jobs.
Note: The Message History works the same for any email sent through the artisan queue:work command. The status in the Message History is set to sent if the email has been sent successfully. If email delivery has failed, the Message History provides an option to re-send the message.
To correctly run this command, run once in your ProcessMaker workspace by using artisan queue:work command. Note that Laravel Queue remains running indefinitely until the job is stopped.
Warning: If you run the command in two terminals for the same workspace, this will bring inconsistencies because both commands point to the same table that stores the queues.
Usage:
[command] (Queue commands) ProcessMaker has extended these commands:
queue:failed-table Create a migration for the failed queue jobs database table.
queue:flush Flush all of the failed queue jobs.
queue:forget Delete a failed queue job.
queue:listen Listen to a given queue.
queue:restart Restart queue worker daemons after their current job.
queue:retry Retry a failed queue job.
queue:table Create a migration for the queue jobs database table.
queue:work Start processing jobs on the queue as a daemon.
Run the following command to see all available Queue commands:
[options] To know the command options, run:
Example:
Note: There are several ways to treat jobs that have failed. For more information, see Queues – Failed Jobs and Dealing With Failed Jobs. And, they will record in the ProcessMaker Standard Logs.
Warning: Not all options can be applied to ProcessMaker because ProcessMaker has its own ORM like the queue:table command.
Alternatively, you can work with a queue monitoring tool to run the artisan command. To do this, read the next section Alternative Queue Monitoring.
Alternative Queue Monitoring for the Artisan Command
To monitor the Queue work in workspaces and to avoid the manual supervision, you can work with Laravel Supervisors in Linux and Windows.
Linux
Follow the next steps to install and configure a Supervisor in an available ProcessMaker - CentOS stack:
Open a terminal and run as a supervisor user by writing the following.
su or sudo -i Install and enable the Supervisor.
yum -y install supervisor systemctl start supervisord systemctl enable supervisord Create the laravel-worker-workflow.ini file in the /etc/supervisord.d/ folder.
nano /etc/supervisord.d/laravel-worker-workflow.ini Do one of the following ways.
- One workspace:
a. Add the following lines and save the file.
[program:laravel-worker-workflow] process_name=%(program_name)s_%(process_num)02d directory=/opt/processmaker/ command=/opt/processmaker/processmaker artisan queue:work --workspace=workflow --sleep=3 --tries=3 --daemon autostart=true autorestart=true user=nginx # Set apache for stacks with this server stdout_logfile=/opt/processmaker/worker-workflow.log b. Enable the laravel-worker-workflow configuration.
supervisorctl reread supervisorctl update supervisorctl start laravel-worker-workflow:* - Two workspaces:
a. Add the following lines and save the file.
[program:laravel-worker-workflow] user = nginx # Set apache for stacks with this server directory = /opt/processmaker/ command = /opt/processmaker/processmaker artisan queue:work --workspace=workflow stdout_logfile= /opt/processmaker/worker-workflow.log autostart=true autorestart=true [program:laravel-worker-sample] user = nginx # Set apache for stacks with this server directory = /opt/processmaker/ command = /opt/processmaker/processmaker artisan queue:work --workspace=sample stdout_logfile= /opt/processmaker/worker-sample.log autostart=true autorestart=true b. Reload the laravel-worker-workflow configuration.
sudo supervisorctl reread sudo supervisorctl update sudo supervisorctl stop all sudo supervisorctl start all sudo supervisorctl status all c. Restart the supervisor to clean possible orphan threads.
sudo systemctl stop supervisord.service sudo systemctl start supervisord.service sudo systemctl status supervisord.service
- One workspace:
The queue work is ready to run.
Take into account:
- Depending on the distribution, the directory route must maintain order. This will specify the processmaker workspace.
- Verify that the configured log file has permissions in the stdout_logfile route. It is recommended that the log file (stdout_logfile) be located within the shared folder of processmaker: /shared/worker.log. This may not be advisable if your environment has many workspaces that have a large workload, your log would be lost in time.
- The parameters of the command route must be valid according to the workload. For more information consult the Laravel documentation.
- Each workspace must have a similar configuration, use the [program: {workspace}] route.
- For {workspace} try to use a format that gives enough information to associate with the installation. For example, [processmaker-workspace instance-domain];. This will allow you to have readability at the supervisor's exit.
- Try using different configuration files for different processmaker environments, with a suitable name for it, you can take the example from the previous point.
- If a failure is present, launch an alert by an email to the administrator.
- Each configuration must be unique per workspace.
- Make sure there are no dead processes running in the background.
- Important: Laravel Queue makes ProcessMaker works heavily. An erroneous configuration can have a considerable impact on performance. Then, be careful and analyze each option referring to the documentation before applying it.
Windows
Follow the next steps to install and configure a Supervisor using NSSM in an available ProcessMaker - Windows Server stack:
Download the latest version of the application from https://nssm.cc/download.
After decompressing the contents of the zip file, copy the nssm.exe file to the folder C:\opt\. This file could be placed anywhere, but it is recommended to place all related to ProcessMaker in the same place.
Open the Windows console as administrator and go to C:\opt\.
Run the command.
nssm install processmaker-jobs-<WORKSPACE> Specify the workspace where the jobs will run. For example:
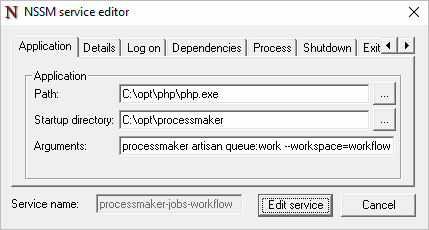
nssm install processmaker-jobs-workflow The last command displays a window with several tabs. Go to the Application tab.
- In the Path field, enter the path where the PHP executable is located, usually C:\opt\php\php.exe.
- In the Startup directory field, enter the path where ProcessMaker is installed, usually C:\opt\processmaker.
- In the Arguments field, enter the queue command specifying the workspace.
processmaker artisan queue:work --workspace=<WORKSPACE>
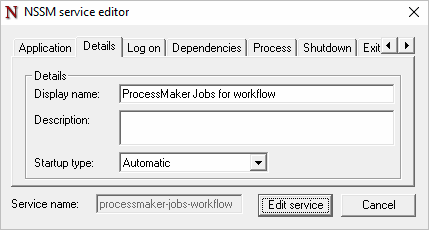
Go to the Details tab. In the Display name field, enter ProcessMaker Jobs for <WORKSPACE>. This value helps ProcessMaker identifies jobs easily in the Windows Services Panel.
Save the configuration. It is not necessary to modify the other fields.
Start the service by running the following command.
nssm start processmaker-jobs-<WORKSPACE> Specify the workspace, for example:
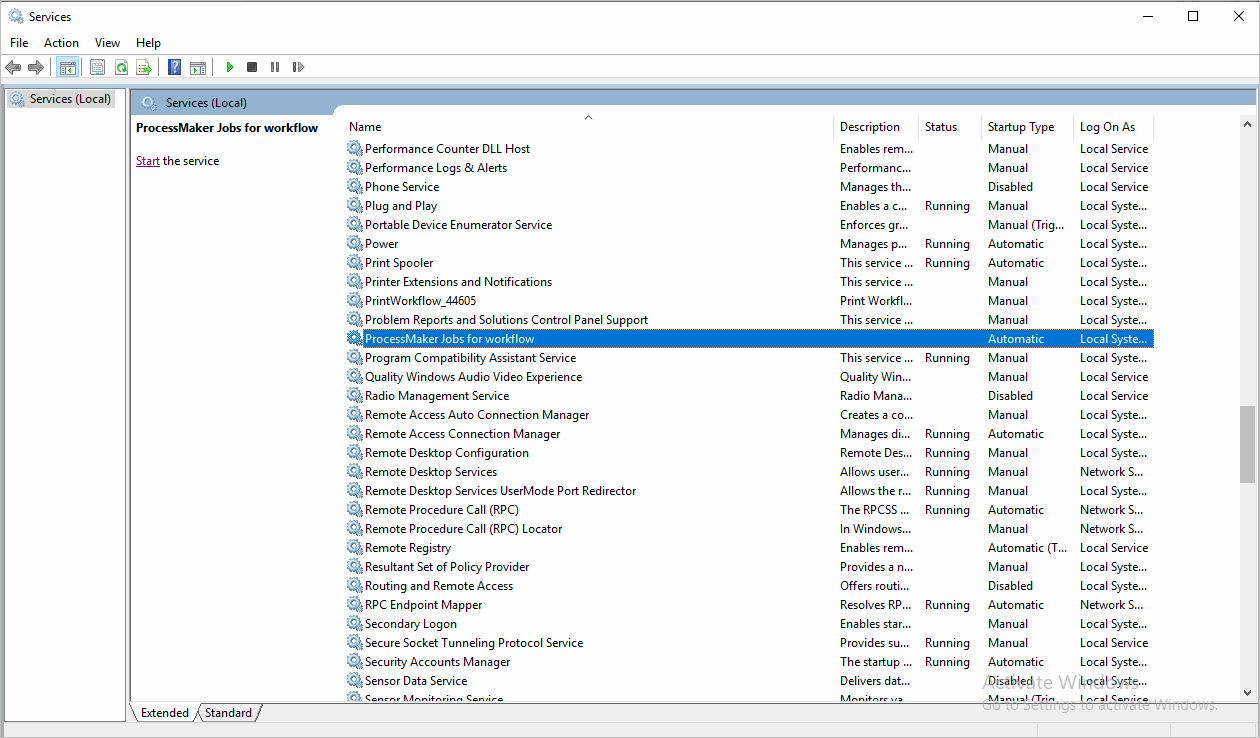
nssm start processmaker-jobs-workflow Alternatively, you can open the Windows Services Panel, and look for the created service and start it, as we can see in the following graphic:
Depending on the Company’s security policies, additionally, in the Log on tab, you can configure the account that will run the service.
browser-cache-files-upgrade
Safe upgrade for files cached by the browser. This command should be run after any upgrade/modification of files cached by the browser.
Example:
build-js
Regenerate ProcessMaker's JavaScript files. This command should be run after any modification of JavaScript files in the gulliver/js/ directory.
Usage:
Options:
-lLANG, --lang=LANGSet the language, such ases(Spanish) orpt-BR(Brazilian Portuguese), to be used when regenerating the JavaScript file. Note that this option currently does not work.
Example:
cacheview-repair
Create and populate the APP_CACHE_VIEW table. In order to improve performance, ProcessMaker includes a cache of cases in the APP_CACHE_VIEW table. This table must be in sync with the list of cases in the APPLICATION and APP_DELEGATION tables to present updated information in the cases list. This command will recreate the table and populate it with the updated information. This only needs to be used after upgrading ProcessMaker or if the cases inbox is out of sync.
Usage:
Options:
-lLANGor--lang=LANG
Specify the language to rebuild the case cache list. If not specified, then 'en' (English) will be used by default.
Ex:-lfr(French)
Ex:--lang=zh-CN(Mainland Chinese)WORKSPACES
Specify the workspaces whose cases cache should be repaired. If no workspace is specified, then the cases will be repaired on all available workspaces.
Example:
change-password-hash-method (Enterprise only)
Set the passwords to use SHA256 or MD5 hashes. See Password Encryption SHA-256.
Usage:
check-queries-incompatibilities
Available Version: As of ProcessMaker 3.4.0.
Check queries incompatibilities (MySQL 5.7) of reserved words for the specified workspace(s).
Usage:
If no workspace is specified, the command will be run in all workspaces. More than one workspace can be specified.
check-workspace-disabled-code (Enterprise only)
Checks any disabled code in the specified workspace(s).
Usage:
If no workspace is specified, the command will be run in all workspaces. More than one workspace can be specified.
Example:
clear-dyn-content-history-data
Available Version: As of ProcessMaker 3.3.0.
Clear History of Use data from the APP_HISTORY table related to the DYN_CONTENT_HISTORY index.
Usage:
Specify the workspace(s) where the History of Use data should be cleared. If no workspace is specified, then the History of Use data will be cleared on all available workspaces.
convert-old-web-entries
Available Version: As of ProcessMaker 3.6.0
Convert Web Entries v1.0 to v2.0 for BPMN processes in order to deprecate the old version. This ProcessMaker command converts all Single Dynaforms to Web Entry multiple steps into a single Dynaform.
Usage:
database-upgrade
Upgrade or repair the database schema to match the installed version of ProcessMaker. This command updates the database to match the schema specified in the files workflow/engine/config/schema.xml and rbac/engine/config/schema.xml.
Use this command to fix databases whose structure has become corrupted or after ProcessMaker has been upgraded, so the database schemas will be changed to match the new ProcessMaker code. This command is executed automatically by processmaker upgrade, but it can be executed separately.
Usage:
Specify the workspaces whose database schema should be upgraded or repaired. Is a known issue if no workspace is specified, then the workspace must be specified.
Example:
database-verify-consistency
Verify that the database data is consistent with the schema, which is specified in the files workflow/engine/config/schema.xml and rbac/engine/config/schema.xml. Use this command to verify the database integrity. Use this command to check the database data consistency before issuing the processmaker database-upgrade or processmaker upgrade commands.
Usage:
Specify the workspace(s) whose database schema should be verified. If no workspace is specified, then all available workspaces will be verified.
Example:
database-verify-migration-consistency
Verify that the migrated case data is consistent and there was no data loss of any kind.
Usage:
Specify the workspace(s) whose case data should be verified for consistency. If no workspace is specified, then all available workspaces will be verified.
This command will check for any missing cases which are Cancelled, Completed, in Inbox and My Inbox (To Do and Draft), Participated, and Unassigned. It is recommended to execute this command if problems occur after importing a workspace or upgrading ProcessMaker.
Example:
documents-add-font
Includes a custom font style into the Rich Text editor for Output Documents.
Usage:
Options:
-
--tinymce: Optional. Allowed values, true or false. This option indicates if the font will be displayed in the Rich Text Editor. Default option is true.Note: To register a family of fonts (Regular, Bold, Italic and Bold Italic), you must register first the regular font with this option set in true and the rest of the fonts with the value false. This is because only the regular font should be displayed in the fonts list in the Rich Text Editor. The association of a family font is made internally (TCPDF resolves this association).
--type: Optional. Allowed values, TrueType or TrueTypeUnicode. TrueTypeUnicode must be used if the font supports unicode characters (such as for Japanese, Chinese, or Russian languages). Default option is TrueType.<FONT-NAME>.ttf: Required. This option must specify the .ttf file of the font that will be added. The font filename is case sensitive.<NAME-IN-MENU>: Optional. This is the text that will be displayed in the editor's dropdown. If the option--tinymceis set to false, this argument is not considered.<ADDITIONAL-ATTRIBUTES>: Optional. if the font requires extra CSS properties (like unicode-range), define these values in this argument (for more details see here). If the option--tinymceis set to false, this argument is not considered.
Example:
documents-list-registered-fonts
Lists all custom registered fonts for Output Documents.
Usage:
Example:
documents-remove-font
Removes a custom font style from Rich Text editor for Output Documents.
Usage:
Options:
<FONT-NAME>.ttf: Required. This option must specify the .ttf file of the font that will be removed. The font filename is case sensitive.
Example:
flush-cache
Flush the cache files for the specified workspace(s).
Usage:
If no workspace is specified, then the cache will be flushed in all available workspaces.
This command deletes the system cache files located in the shared/compiled directory. It also deletes the workspace cache files located in the shared/sites/WORKSPACE/cache/ and shared/sites/WORKSPACE/cachefiles/ directories. Any deleted cache files will be regenerated when needed by ProcessMaker. This command is useful after installing or updating a new PO translation file or when the cache copy of forms gets corrupted.
Note: If the flush-cache command is executed after creating an endpoint, the new endpoint is automatically regenerated.
Example:
hotfix-install
Install a hotfix or patch in the ProcessMaker code.
Usage:
This command installs a hotfix or patch, which updates ProcessMaker in order to add improvements, fix bugs and security holes and change the database schema. Hotfixes are generally only available for the Enterprise Edition. See: How to install a Hotfix or a Patch.
info
Print information about the current system and any specified workspaces.
Usage:
If no workspace is specified, show information about all available workspaces
Example:
mafe-translation
Creates translation labels in the Michealangelo Font End (MAFE) which are inserted in the database. This command should be run after adding or deleting translation labels in ProcessMaker's JavaScript code.
Usage:
If no workspace is specified, then the translation labels will be created in all available workspaces.
Options:
-lLANG, --lang=LANGSpecify the language to create the translation labels. If not specified then the language will be 'en' (English) by default.
Ex:-lfr(French)
Ex:--lang=zh-CN(Mainland Chinese)
Example:
migrate-cases-folders
Migrate the cases folders of the workspace to break the directory for each case into multiple subdirectories to avoid problems with Ext3 file systems which are limited to 32K subdirectories. See: Managing 32K Folders.
Usage:
Options:
-wWORKSPACE,--workspace=WORKSPACE
Select the workspace whose case folders will be migrated, if multiple workspaces are present in the server.
Ex:-wworkflow
Ex:--workspace=workflow
In version 3, all installations already have broken the case directories into multiple subdirectories, so this command only needs to be used if ProcessMaker was originally installed in version 2. Upgrading to version 3 won't automatically split the case directories to avoid the 32K limit in Ext3.
Example:
migrate-content
Most of the names/titles of objects are currently stored in the CONTENT table in the database. In order to speed up accessing the names of groups, departments, processes, tasks and Input Documents, fields were added to a number of database tables in version 3.1, so it was no longer necessary to do separate queries in the CONTENT. If necessary, the migrate-content option adds new fields to the various tables to hold the names/titles from the CONTENT table. It also copies the names/titles from the CONTENT table to the many different tables. Use this command if upgrading ProcessMaker 3.1 or later from a previous version of ProcessMaker or if the content gets out of sync.
Usage:
Specify the workspace(s) where the content should be migrated. If no workspace is specified, then the content will be migrated on all available workspaces.
Example:
migrate-content Options:
The options to run the migrate-content command in a console are the following:
- --lang
Specify a language to migrate content. If no language is specified, then the content will be migrated using the default language.
Ex../processmaker migrate-content --lang=en This command migrates content on all available workspaces, in English. - WORKSPACE
Specify the WORKSPACE where the content will be migrated. If no workspace is specified, then the content will be migrated on all available workspaces.
Ex../processmaker migrate-content WORKSPACE This command migrates content to default language on this WORKSPACE - --lang + WORKSPACE
It is possible to combine previous parameters, first specify the language to migrate the content, then specify the workspace where the content will be migrated.
Ex../processmaker migrate-content --lang=en WORKSPACE This command migrates content on this WORKSPACE, in English.
migrate-history-data
Available Version: As of ProcessMaker 3.3.0.
Migrate the content of the APP_HISTORY table to the APP_DATA_CHANGE_LOG table. Execute this command after executing the upgrade command.
Usage:
Specify the workspace(s) where the history data should be migrated. If no workspace is specified, then the history data will be migrated on all available workspaces.
Options:
This parameter can be included ONLY if in the table APP_HISTORY, in the column of HISTORY_DATA, it does not contain the key DYN_CONTENT_HISTORY, because cleaning this field requires more time in the execution of the upgrade.
migrate-indexing-acv
Increases the performance populating with integer values the new columns created in APP_* tables by the migrate-new-cases-lists command. This command must be run after migrate-new-cases-lists.
migrate-itee-to-dummytask
Migrates the Intermediate throw Email Event to Dummy task.
Usage:
Specify the workspaces where the processes will be updated. If no workspace is specified, then all available workspaces will be updated.
Example:
migrate-list-unassigned (Enterprise only)
Migrates information in the APP_CACHE_VIEW table in the database to the LIST_UNASSIGNED table, so that the "Unassigned" list of cases under the Home menu can be loaded more quickly. Use this command if upgrading the Enterprise Edition to version 3.1 or later.
Usage:
Specify the workspace(s) where the APP_CACHE_VIEW table will be updated. If no workspace is specified, then all available workspaces will be processed.
Example:
migrate-new-cases-lists (Enterprise only)
Migrate the case list information found in the APPLICATION and APP_DELEGATION tables to the new LIST_* tables found in version 3.1 and later, so that case lists under the Home menu can be loaded faster in the Enterprise Edition.
Usage:
Specify the WORKSPACE where the case information will be migrated to the LIST_* tables. More than one workspace can be specified. If no workspace is specified, then case information in all available workspaces will be migrated to the LIST_* tables.
migrate-plugins-singleton-information
Migrate the singleton information file to the PLUGINS_REGISTRY table found in version 3.2.2 and later, so that the information about plugins can be loaded faster.
Usage:
plugins-database-upgrade
Upgrade or repair the database schema to match the latest version of a plugin. Run this command after upgrading the source code for a plugin. The database schema file for a plugin is found at the location plugins/pluginName/pluginName/config/schema.xml.l
Usage:
Specify the workspaces whose database should be upgraded or repaired to match the schema files of all its available plugin(s). If no workspace is specified, then the database schema will be upgraded or repaired on all available workspaces.
This is the same as the database-upgrade command, but it works with the schema files provided by plugins. This is useful if plugins are installed that include database schemas.
plugins-translation-create
Create a .po translation file for a specified plugin. After the .po file is generated, it can be translated into another language and then imported into ProcessMaker so that the plugin is available in another language.
Usage:
PLUGIN is the name of the plugin directory. If not specified, then translation files will be created for all available plugins.
LANG is the language for which the .po file will be generated, such as fr (French) or zh-CN (mainland Chinese). If the language is not specified, then it is en (English) by default.
plugins-translation-update
Update plugin translations
Usage:
PLUGIN is the name of the plugin directory.
LANG is the language, such as fr (French) or zh-CN (mainland Chinese).
remove-unused-files
Available Version: As of ProcessMaker 3.3.12.
Remove deprecated files.
Usage:
The user who executes this command must have the permission to delete files.
translation-repair
Upgrade or repair translations for the specified workspace(s).
Usage:
If no workspace is specified, the command will be run in all workspaces. More than one workspace can be specified.
This command will go through each language installed in ProcessMaker and update the translations for the workspace(s) to match the current version of ProcessMaker.
unify-database (Enterprise only)
Unify the RBAC, Reports and Workflow databases into one database.
Usage:
Specify the workspaces whose databases schemas should be unified. If no workspace is specified, then the database schema will be upgraded or repaired on all available workspaces.
This command will read the system schema and attempt to modify the workspaces' tables to match this new schema. In version 2.8 and later, it will merge the 3 databases used in previous versions of ProcessMaker into one database. This command may be used after upgrading from ProcessMaker 2.5 to a later version of ProcessMaker.
upgrade
Upgrade workspaces.
Usage:
This command should be run after upgrading ProcessMaker to a new version so that all workspaces are also upgraded to the new version.
Options:
-ACV,--buildACV
If this option is enabled, the Cache View in the APP_CACHE_VIEW table is built.-NoXml,--no-xml
If this option is enabled, the XML files translation is not built.-i,--keep_dyn_content
Available Version: This option is available as of ProcessMaker 3.3.0.
Include the DYN_CONTENT_HISTORY value. Keeps APP_HISTORY data that is in the DYN_CONTENT_HISTORY table.
Note: Using the --keep_dyn_content option keeps APP_HISTORY data but in the future might require clearing the DYN_CONTENT_HISTORY table. For this purpose use the clear-dyn-content-history-data command.
upgrade-content
Upgrade the Content table of specified workspace(s).
Usage:
If no workspace is specified, the command will be run in all workspaces. More than one workspace can be specified.
Note: This command is executed only if all labels of the corresponding tables are migrated.
workspace-backup
Backup the specified workspace to a file. For more information, see Backing up ProcessMaker.
Usage:
WORKSPACE is the name of the workspace to backup, which by default is named workspace.
BACKUP-FILE is the backup filename which will be created. If it contains slashes, it will be treated as a path and filename, either absolute or relative. Otherwise, it will be treated as a filename located inside the shared/backups directory. If no BACKUP-FILE is specified, it will use the workspace name as the filename.
A backup archive will contain all information about the specified workspace so that it can be restored later. The archive includes a database dump and all the workspace files.
Options:
-s[MAX-SIZE],--filesize=[MAX-SIZE]
Split the backup file in multiple files which are compressed. The maximum size of these files is set to MAX-SIZE in megabytes. If MAX-SIZE is not set, then it is 1000 megabytes by default. It may be necessary to use this option if using a 32 bit Linux/UNIX system which limits its maximum file size to 2GB. This option does not work on Windows systems.
workspace-restore
Restore a workspace from a backup file. For more information, see Restoring Workspaces.
Usage:
BACKUP-FILE is the backup filename. If it contains slashes, it will be treated as a path and filename, either absolute or relative. Otherwise, it will be treated as a filename located inside the shared/backups directory.
Specify the WORKSPACE to restore to a different workspace name. Otherwise, it will restore to the same workspace name as the original backup.
Options:
-o,--overwrite
If a workspace already exists, then overwrite it.-i
Show information about backup file, but do not restore any workspaces.-m
Restore from multiple compressed backup files which are numbered. This is an option for Linux/UNIX systems which limit files to a maximum of 2 GB in size.-wWORKSPACE,--workspace=WORKSPACE
Specify which workspace to restore if multiple workspaces are present in the backup file.
Ex:-wworkflow-lLANG,--lang=LANG
Specify the language which will be used to rebuild the case cache list. If this option isn't included, thenen(English) will be used by default.-pPORT
Specify the port number used by MySQL. If not specified, then the port 3306 will be used by default.
Ex:-p3882
Warning: To correctly run the workspace-restore command, take into account the following:
- All folders and files of the restored workspace must have the same permissions as in the shared folder.
- As of ProcessMaker 3.5.0, after exhausting the memory limit using this command
workspace-restore, the IT Administrator must increase thememory_limitin the php.ini file to at least512M.
workspace-upgrade
Upgrade the specified workspace(s). Use this command after upgrading the source code of ProcessMaker.
Usage:
If no workspace is specified, the command will be run in all workspaces. More than one workspace can be specified.
This command is a shortcut to execute all the upgrade commands for workspaces. Upgrading a workspace will make the database and files correspond to the current source code of ProcessMaker.
Options:
-ACV,--buildACV
If this option is enabled, the APP_CACHE_VIEW table will be built, which allows ProcessMaker to load case lists more quickly.-NoXml,--no-xml
If this option is enabled, then the XML files translation is not built.



